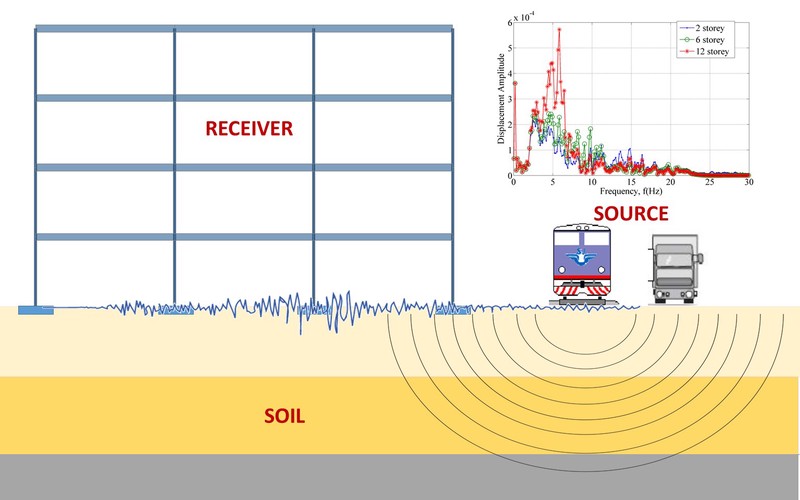
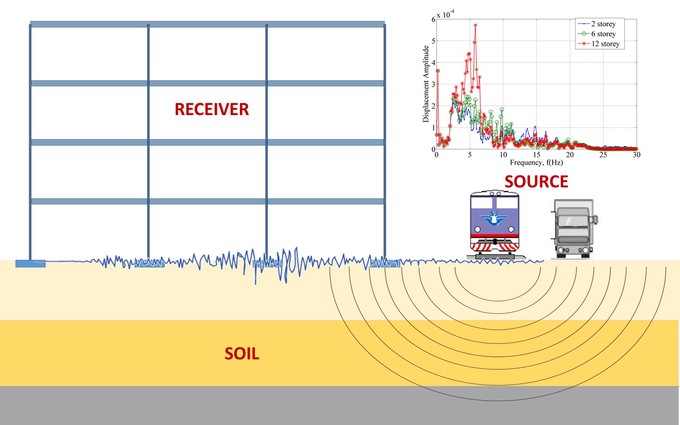
Vibrations induced by traffic propagate through the soil medium, reaching the foundations of surrounding structures and causing them to vibrate. Modelling and prediction of traffic-induced vibrations is complex and requires the following issues to be addressed properly: emission (excitation by traffic), transmission (wave propagation through the soil), and immission (transfer of excitation into a building). Most of the available numerical methods are based on the substructure approach where the soil-structure domain is decomposed in two subdomains: the unbounded domain - soil and the bounded domain – structure. The subdomains are modelled separately, while the interaction is accomplished through the compatibility of the interface between the subdomains.
Main research activities in this field are focused toward the development of numerical models to predict the response multistorey frame structures subjected to traffic-induced vibration. The analysis is carried out in the frequency domain using the substructure method. The structure is modelled using
dynamic stiffness elements,
while the dynamic stiffness matrix of the soil is calculated using the
integral transform method.
It is assumed that the foundations are rigid, and that they rest on the surface of an elastic half space. An original software in MATLAB has been developed, enabling vibration response analysis of multisorey frames accounting for soil-structure interaction.